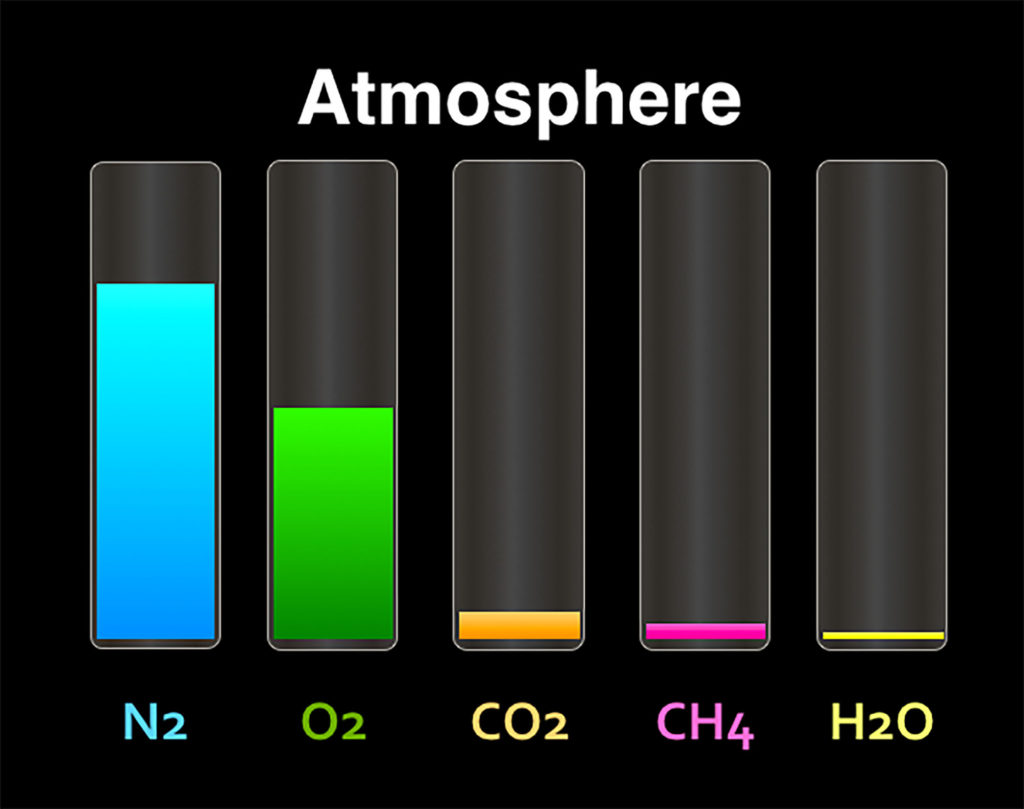
Mixing Different Types Of Gas . we can use the ideal gas law to describe the pressures of both gas \(a\) and the mixture: \(p_a = n_art/v\) and \(p_{tot} = n_trt/v\). Tecline mixtures are delivered with a standard. The ratio of the two is thus \[\dfrac{p_a}{p_{tot}}=\dfrac{n_art/v}{n_{tot}rt/v} = \dfrac{n_a}{n_{tot}}=x_a \label{6.6.6}\] When they do so, they become a solution—a homogeneous mixture. the pressure exerted by each gas in a gas mixture (its partial pressure) is independent of the pressure exerted by all other gases. these categories define the tolerance, uncertainty and stability period: by convention, the process of mixing two gases, call them \(a\) and \(b\), is the process in which the two gases initially occupy separate containers, but are both at a common pressure and temperature. one of the properties of gases is that they mix with each other. Some of the properties of.
from exouuhrau.blob.core.windows.net
\(p_a = n_art/v\) and \(p_{tot} = n_trt/v\). Some of the properties of. by convention, the process of mixing two gases, call them \(a\) and \(b\), is the process in which the two gases initially occupy separate containers, but are both at a common pressure and temperature. The ratio of the two is thus \[\dfrac{p_a}{p_{tot}}=\dfrac{n_art/v}{n_{tot}rt/v} = \dfrac{n_a}{n_{tot}}=x_a \label{6.6.6}\] When they do so, they become a solution—a homogeneous mixture. the pressure exerted by each gas in a gas mixture (its partial pressure) is independent of the pressure exerted by all other gases. we can use the ideal gas law to describe the pressures of both gas \(a\) and the mixture: one of the properties of gases is that they mix with each other. Tecline mixtures are delivered with a standard. these categories define the tolerance, uncertainty and stability period:
Different Kinds Of Gasses at Linda Litteral blog
Mixing Different Types Of Gas the pressure exerted by each gas in a gas mixture (its partial pressure) is independent of the pressure exerted by all other gases. the pressure exerted by each gas in a gas mixture (its partial pressure) is independent of the pressure exerted by all other gases. one of the properties of gases is that they mix with each other. Tecline mixtures are delivered with a standard. When they do so, they become a solution—a homogeneous mixture. Some of the properties of. these categories define the tolerance, uncertainty and stability period: we can use the ideal gas law to describe the pressures of both gas \(a\) and the mixture: The ratio of the two is thus \[\dfrac{p_a}{p_{tot}}=\dfrac{n_art/v}{n_{tot}rt/v} = \dfrac{n_a}{n_{tot}}=x_a \label{6.6.6}\] \(p_a = n_art/v\) and \(p_{tot} = n_trt/v\). by convention, the process of mixing two gases, call them \(a\) and \(b\), is the process in which the two gases initially occupy separate containers, but are both at a common pressure and temperature.
From www.youtube.com
mixing of gases YouTube Mixing Different Types Of Gas these categories define the tolerance, uncertainty and stability period: \(p_a = n_art/v\) and \(p_{tot} = n_trt/v\). When they do so, they become a solution—a homogeneous mixture. Some of the properties of. Tecline mixtures are delivered with a standard. one of the properties of gases is that they mix with each other. the pressure exerted by each gas. Mixing Different Types Of Gas.
From byjus.com
Air is a compound of different gases. Mixing Different Types Of Gas we can use the ideal gas law to describe the pressures of both gas \(a\) and the mixture: The ratio of the two is thus \[\dfrac{p_a}{p_{tot}}=\dfrac{n_art/v}{n_{tot}rt/v} = \dfrac{n_a}{n_{tot}}=x_a \label{6.6.6}\] \(p_a = n_art/v\) and \(p_{tot} = n_trt/v\). the pressure exerted by each gas in a gas mixture (its partial pressure) is independent of the pressure exerted by all other. Mixing Different Types Of Gas.
From sabotin.ung.si
Gas mixing and distribution Mixing Different Types Of Gas these categories define the tolerance, uncertainty and stability period: one of the properties of gases is that they mix with each other. the pressure exerted by each gas in a gas mixture (its partial pressure) is independent of the pressure exerted by all other gases. by convention, the process of mixing two gases, call them \(a\). Mixing Different Types Of Gas.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT SIMPLE MIXTURES thermodynamic description of mixtures PowerPoint Mixing Different Types Of Gas Some of the properties of. by convention, the process of mixing two gases, call them \(a\) and \(b\), is the process in which the two gases initially occupy separate containers, but are both at a common pressure and temperature. one of the properties of gases is that they mix with each other. When they do so, they become. Mixing Different Types Of Gas.
From saylordotorg.github.io
Mixtures of Gases Mixing Different Types Of Gas we can use the ideal gas law to describe the pressures of both gas \(a\) and the mixture: the pressure exerted by each gas in a gas mixture (its partial pressure) is independent of the pressure exerted by all other gases. The ratio of the two is thus \[\dfrac{p_a}{p_{tot}}=\dfrac{n_art/v}{n_{tot}rt/v} = \dfrac{n_a}{n_{tot}}=x_a \label{6.6.6}\] one of the properties of. Mixing Different Types Of Gas.
From exouuhrau.blob.core.windows.net
Different Kinds Of Gasses at Linda Litteral blog Mixing Different Types Of Gas When they do so, they become a solution—a homogeneous mixture. these categories define the tolerance, uncertainty and stability period: The ratio of the two is thus \[\dfrac{p_a}{p_{tot}}=\dfrac{n_art/v}{n_{tot}rt/v} = \dfrac{n_a}{n_{tot}}=x_a \label{6.6.6}\] one of the properties of gases is that they mix with each other. \(p_a = n_art/v\) and \(p_{tot} = n_trt/v\). we can use the ideal gas law. Mixing Different Types Of Gas.
From examples.yourdictionary.com
Examples of Homogeneous Mixtures Solid, Liquid and Gas YourDictionary Mixing Different Types Of Gas we can use the ideal gas law to describe the pressures of both gas \(a\) and the mixture: When they do so, they become a solution—a homogeneous mixture. \(p_a = n_art/v\) and \(p_{tot} = n_trt/v\). one of the properties of gases is that they mix with each other. these categories define the tolerance, uncertainty and stability period:. Mixing Different Types Of Gas.
From www.esrf.eu
Gas mixing system Mixing Different Types Of Gas Some of the properties of. these categories define the tolerance, uncertainty and stability period: \(p_a = n_art/v\) and \(p_{tot} = n_trt/v\). by convention, the process of mixing two gases, call them \(a\) and \(b\), is the process in which the two gases initially occupy separate containers, but are both at a common pressure and temperature. the pressure. Mixing Different Types Of Gas.
From www.manufacturingtomorrow.com
Complete Guide to Gas Mixing and Blending ManufacturingTomorrow Mixing Different Types Of Gas The ratio of the two is thus \[\dfrac{p_a}{p_{tot}}=\dfrac{n_art/v}{n_{tot}rt/v} = \dfrac{n_a}{n_{tot}}=x_a \label{6.6.6}\] we can use the ideal gas law to describe the pressures of both gas \(a\) and the mixture: one of the properties of gases is that they mix with each other. by convention, the process of mixing two gases, call them \(a\) and \(b\), is the. Mixing Different Types Of Gas.
From www.yourdictionary.com
Examples of Heterogeneous Mixtures Types Made Simple YourDictionary Mixing Different Types Of Gas these categories define the tolerance, uncertainty and stability period: one of the properties of gases is that they mix with each other. Tecline mixtures are delivered with a standard. by convention, the process of mixing two gases, call them \(a\) and \(b\), is the process in which the two gases initially occupy separate containers, but are both. Mixing Different Types Of Gas.
From www.pctflow.com
Gas mixing systems Static mixers and Integrated systems Mixing Different Types Of Gas When they do so, they become a solution—a homogeneous mixture. the pressure exerted by each gas in a gas mixture (its partial pressure) is independent of the pressure exerted by all other gases. one of the properties of gases is that they mix with each other. Tecline mixtures are delivered with a standard. \(p_a = n_art/v\) and \(p_{tot}. Mixing Different Types Of Gas.
From www.haikudeck.com
Gases Lesson by Teresa Gonzalez Mixing Different Types Of Gas Tecline mixtures are delivered with a standard. Some of the properties of. these categories define the tolerance, uncertainty and stability period: \(p_a = n_art/v\) and \(p_{tot} = n_trt/v\). the pressure exerted by each gas in a gas mixture (its partial pressure) is independent of the pressure exerted by all other gases. by convention, the process of mixing. Mixing Different Types Of Gas.
From chemistryguru.com.sg
Ideal Gas Law and Applications Mixing Different Types Of Gas the pressure exerted by each gas in a gas mixture (its partial pressure) is independent of the pressure exerted by all other gases. The ratio of the two is thus \[\dfrac{p_a}{p_{tot}}=\dfrac{n_art/v}{n_{tot}rt/v} = \dfrac{n_a}{n_{tot}}=x_a \label{6.6.6}\] Some of the properties of. \(p_a = n_art/v\) and \(p_{tot} = n_trt/v\). Tecline mixtures are delivered with a standard. by convention, the process of. Mixing Different Types Of Gas.
From www.azom.com
Gas Mixing Applications Mixing Different Types Of Gas one of the properties of gases is that they mix with each other. these categories define the tolerance, uncertainty and stability period: we can use the ideal gas law to describe the pressures of both gas \(a\) and the mixture: The ratio of the two is thus \[\dfrac{p_a}{p_{tot}}=\dfrac{n_art/v}{n_{tot}rt/v} = \dfrac{n_a}{n_{tot}}=x_a \label{6.6.6}\] Tecline mixtures are delivered with a. Mixing Different Types Of Gas.
From www.youtube.com
Ideal gas mixtures 1 YouTube Mixing Different Types Of Gas the pressure exerted by each gas in a gas mixture (its partial pressure) is independent of the pressure exerted by all other gases. by convention, the process of mixing two gases, call them \(a\) and \(b\), is the process in which the two gases initially occupy separate containers, but are both at a common pressure and temperature. \(p_a. Mixing Different Types Of Gas.
From www.researchgate.net
Gas mixing and filling system Download Scientific Diagram Mixing Different Types Of Gas \(p_a = n_art/v\) and \(p_{tot} = n_trt/v\). The ratio of the two is thus \[\dfrac{p_a}{p_{tot}}=\dfrac{n_art/v}{n_{tot}rt/v} = \dfrac{n_a}{n_{tot}}=x_a \label{6.6.6}\] we can use the ideal gas law to describe the pressures of both gas \(a\) and the mixture: Tecline mixtures are delivered with a standard. When they do so, they become a solution—a homogeneous mixture. the pressure exerted by each. Mixing Different Types Of Gas.
From www.thoughtco.com
List 10 Types of Solids, Liquids, and Gases Mixing Different Types Of Gas we can use the ideal gas law to describe the pressures of both gas \(a\) and the mixture: one of the properties of gases is that they mix with each other. by convention, the process of mixing two gases, call them \(a\) and \(b\), is the process in which the two gases initially occupy separate containers, but. Mixing Different Types Of Gas.
From psctexas.com
Gas Mixing for Homogeneous Gas Mixtures PSC Texas Mixing Different Types Of Gas we can use the ideal gas law to describe the pressures of both gas \(a\) and the mixture: Tecline mixtures are delivered with a standard. the pressure exerted by each gas in a gas mixture (its partial pressure) is independent of the pressure exerted by all other gases. When they do so, they become a solution—a homogeneous mixture.. Mixing Different Types Of Gas.